Therapeutic Ultrasound with Piezo Components
Ultrasound opens up new and innovative therapeutic possibilities that improve or even substitute many established procedures: Minimally invasive and gentle treatment methods with improved therapy success and fewer side effects can be realized using piezo components.
Therapeutic ultrasound refers to methods in which ultrasound is not only a means of diagnosis but also the core element of the therapy, e. g. tissue ablation, targeted drug delivery, ultrasound-assisted thrombolysis, and lithotripsy.
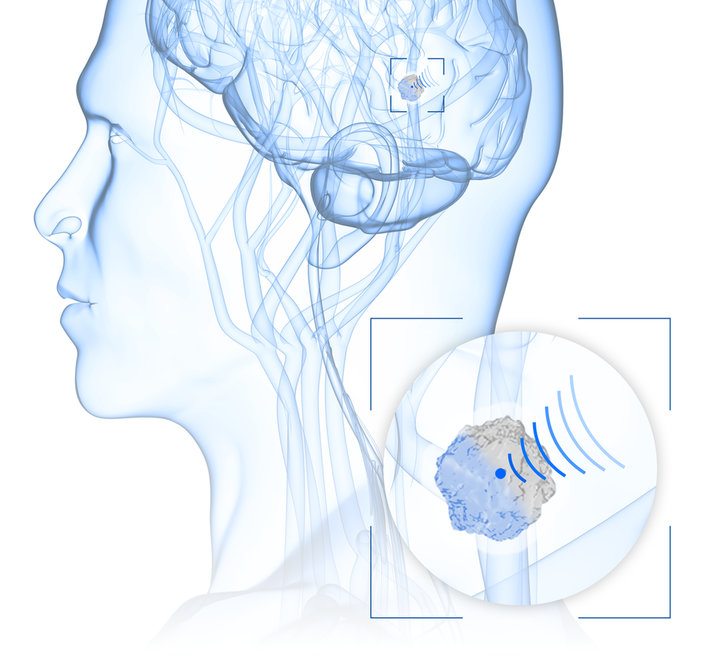
HIFU for Noncontact Tissue Ablation
The ultrasound-based ablation of tissue, for example for the removal of tumors in the prostate or uterus, is carried out extracorporeal and is thus noninvasive. For this therapy, high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) is projected into the body with the help of piezoelectric elements. Piezo discs, plates, and focus bowls by PI Ceramic are manufactured in customer-specific geometries and electrode designs and are ideally suited for building HIFU transducers.
In order to generate a directed wave, several of the piezoelectric elements are arranged on a spherical dome and excited synchronously to focus the energy in the shock wave.
These acoustic waves have various effects in the body: In histotripsy, ultrasound produces cavitation bubbles whose mechanical energy causes cells to burst. Thermal ablation using ultrasound generates heat of over 42°C by absorbing the wave energy so that the proteins of the cell structures become denaturated and entire tissue areas are coagulated in the sound focus.
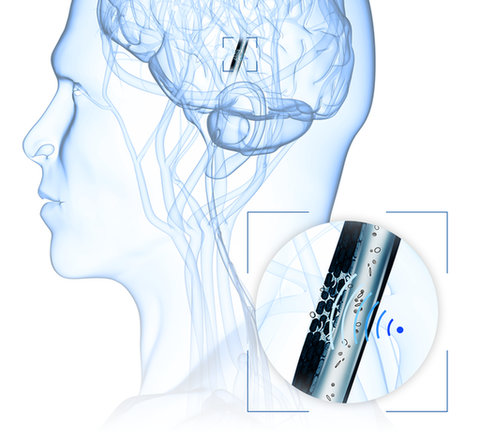
Targeted Drug Delivery:
Drug Application within the Body
Another use case for HIFU generation with piezoelectric discs, plates, and focus bowls are targeted drug delivery procedures. Using HIFU, drugs can be released or activated at a specific site in the body.
The basic method is the injection of microspheres filled with medication or gas, which are distributed in the patient's bloodstream during treatment and are only used where they are in the sound field focus.
An unstable cavitation caused by ultrasound causes the microspheres to burst and the medication to be released locally.
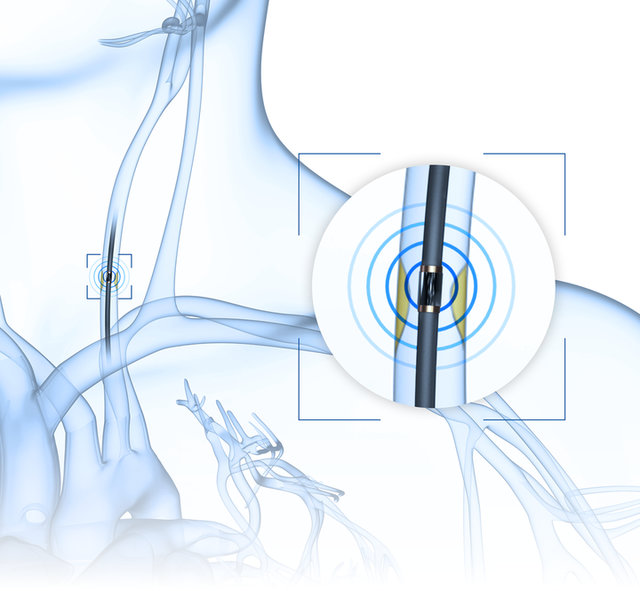
Intravascular Lithotripsy with Miniaturized Piezo Components
Intravascular lithotripsy is used in a minimally invasive way to reduce atherosclerotic plaques in blood vessels or at the heart valves as well as life-threatening stenoses.
Ultrasound waves increase the permeability of the blood vessel wall through sonoporation so that the medication can penetrate better and induce the dissolution of plaques.
If a thrombus has already formed, its structure can be loosened with the help of mechanical ultrasound energy.
This makes it easier for drugs to penetrate into the thrombus and dissolve it, ensuring the flow of blood to vital organs and preventing embolisms.
Miniaturized piezo tubes or tiny plates are used for intravascular lithotripsy and thrombectomy applications as they can generate ultrasound waves even when integrated into the finest catheters.

PI Ceramic manufactures piezo elements with dimensions of less than one millimeter.
About PI Ceramic GmbH
Redefining the limits of what can be measured and moved, together with our customers: As a worldwide partner with more than 25 years of expertise, PI Ceramic develops and manufactures sophisticated piezoceramic components and subsystems in the areas of medical technology, industrial ultrasonic sensors and precision dosing. Seventy of the currently 320 employees at the location in Thuringia, Germany, work in research and development. PI Ceramic is part of the PI Group, the innovation and market leader for high-precision positioning technology.
BACK TO TOP