Company Insight
Sponsored by Alleima
Precision in heat
The role of thermocouples in modern medical devices
Main image: A thermocouple is a temperature sensor formed by joining two dissimilar metal wires at one end. When this junction experiences a temperature change, it generates a voltage,
described as the Seebeck effect. Credit: Alleima

Dr. Bernd Vogel
In the evolving landscape of medical technology, precision and reliability are paramount. Among the unsung heroes enabling this precision are thermocouple wires—tiny, self-powered sensors that play a critical role in temperature monitoring across a wide spectrum of medical applications. As devices become smarter and more miniaturized, thermocouples are increasingly vital for ensuring patient safety and therapeutic efficacy.
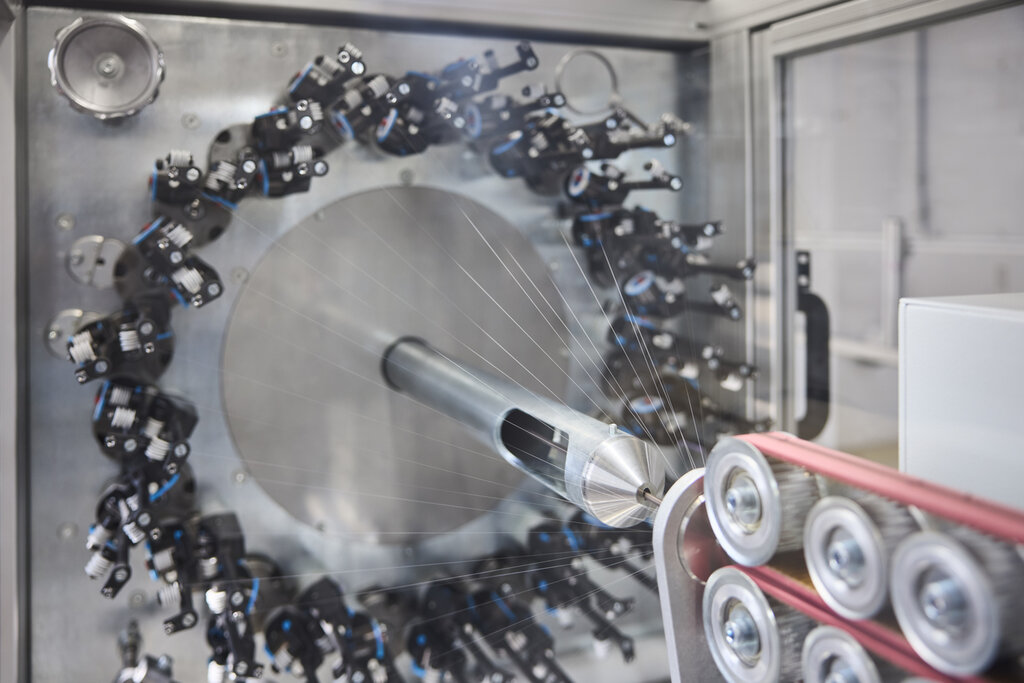

Braiding is one of Alleima’s core capabilities in nitinol processing. Others include laser-cutting, shaping, grinding, joining, and cleanroom assembling. Credit: Alleima
Nitinol's versatility has led to its use in a wide array of medical devices. In addition to guidewires, nitinol is used in flexible retrieval devices and instruments, vascular filters, and permanent implants. These devices benefit from nitinol's ability to endure repeated stress without losing shape or performance. Nitinol’s adaptability allows it to be crimped, bent, or coiled into tight configurations, easing insertion through minimally invasive methods. In cardiovascular treatments, nitinol filters capture blood clots and prevent embolisms. These filters collapse for deployment and expand inside blood vessels to perform life-saving functions. Nitinol is also promising in steerable medical devices like endoscopes and catheters.
However, manufacturing nitinol in a cost-effective way while maintaining the highest quality requires specialist capabilities. Even the slightest deviation during production can alter the performance of the material. Understanding the impact of cold work, heat treatment, strain rate, and number of cycles is essential for optimizing the stress-strain behavior of nitinol.
Having acquired long-standing nitinol expertise with Endosmart in 2022 and Endox in 2024, Alleima combines decades of expertise in material science with leading know-how in nitinol processing, delivering wire-based solutions and medical components designed to meet the exacting demands of modern surgery. Whether it’s developing steerable devices for robotic surgery or advanced, flexible instruments and implants for various applications, including urology, gastroenterology, oncology or cardiovascular, Alleima’s collaborative approach ensures its clients can navigate the complexities of nitinol manufacturing with ease, highest quality, and functionality of its solutions all the way to market approval.
In a field where every innovation can translate into saved lives and improved patient outcomes, access to expert knowledge is invaluable. To learn more about Alleima's engineering services and processing capabilities in nitinol, visit their website, Nitinol—shaping the future—Alleima, where you can also download their nitinol whitepaper Nitinol and its transformative role in medical devices.

Dr. Bernd Vogel

Braiding and Twisting detail center. Credit: Alleima
Understanding Thermocouples
A thermocouple is a temperature sensor formed by joining two dissimilar metal wires at one end. When this junction experiences a temperature change, it generates a voltage via the Seebeck effect. This voltage is then interpreted by medical systems to infer temperature with high accuracy. Unlike other sensors, thermocouples are self-powered and require no external power source, making them ideal for confined and invasive applications
Medical-grade thermocouples are engineered for superior precision and miniaturization. Their tight tolerances and consistent performance allow for seamless integration into devices such as catheters, probes, and surgical tools, enabling real-time temperature monitoring during procedures.
Thermocouple in multifilar setups, allowing for multiple sensing junctions or integration with other conductors. Credit: Alleima
When asked to simply describe the shape-memory effect, Dr. Bernd Vogel takes out a wire shaped like a heart, straightens it completely, and then slowly dips it into a cup of hot coffe. Immidately the wire returns to its perfect heart shape.
Types of thermocouples in medicine
Different metal pairings yield different thermocouple types, each with unique characteristics. Type T (copper-constantan) is favoured for cryoablation and body temperature monitoring due to its accuracy in low-temperature ranges. Type K (chromel-alumel) offers a broader temperature span, suitable for sterilization and high-heat environments. Type E and Type N provide rapid response and stability, ideal for mid-range applications and electromagnetically sensitive settings.
Thermocouple types are standardized by international bodies in codes such as ASTM E230 and IEC 60584, ensuring interoperability and calibration consistency across devices.
Engineering for medical use
The design of medical thermocouple wires demands meticulous attention to materials and construction. Wires are often drawn to ultrafine diameters—down to 0.025mm (0.000984 in), thinner than a human hair—allowing integration into the narrowest lumens of catheters or needles. Insulation materials like polyimide, poly-nylon, and polyesterimide are chosen for their biocompatibility and resistance to sterilization methods such as autoclaving, ethylene oxide gas, and gamma irradiation
Configurations range from bifilar (two wires) to multifilar setups, which may include redundant pairs or additional conductors for multifunctional use. Some wires come pre-packaged with encapsulated junctions, simplifying integration and ensuring consistent thermal response.
Applications in Medical Devices
Cardiac ablation
Thermocouples are integral to radiofrequency (RF) ablation catheters used to treat arrhythmias. Embedded in the catheter tip, they monitor tissue temperature in real time, allowing RF generators to modulate power and prevent overheating. In cryoablation, thermocouples ensure the tissue reaches and maintains the target freezing temperature, avoiding ineffective lesions or tissue damage.
Renal denervation
In catheter-based treatments for drug-resistant hypertension, thermocouples regulate energy delivery during sympathetic nerve ablation in the renal arteries. They help prevent overheating and ensure precise targeting, especially in systems using ultrasound energy.
Oncology and tumour ablation
Thermocouples are widely used in interventional oncology for RF, cryo, microwave, and ultrasound ablation. They provide feedback to control energy delivery, ensuring complete tumour destruction while minimizing damage to surrounding tissues. Cryoablation probes often include multiple sensors to monitor the extent of freezing, while microwave and ultrasound systems rely on thermocouples for real-time thermal control.
Duodenal mucosal resurfacing
This emerging therapy for metabolic diseases like type 2 diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease uses thermal ablation to regenerate the duodenal lining. Thermocouples ensure precise temperature control during the procedure, safeguarding surrounding tissues.
Pain management and neuromodulation
RF neurotomy for chronic pain conditions such as facet joint arthritis and trigeminal neuralgia depends on thermocouples to create accurate heat lesions. These sensors prevent excessive heating and collateral damage, enhancing both safety and efficacy.
Gynecological therapies
Endometrial ablation procedures use thermocouples to monitor and regulate temperature during RF, cryotherapy, or heated fluid treatments. They help maintain uniform ablation and activate safety shutoffs if temperatures exceed safe thresholds.
Critical care and equipment monitoring
Thermocouples are embedded in ventilators, incubators, sterilizers, and dialysis machines to monitor and control temperature. In neonatal care, they help maintain thermoneutral environments. In imaging systems like MRI and CT scanners, they prevent overheating of critical components. Laboratory equipment also uses thermocouples to ensure safe storage conditions for blood, vaccines, and reagents.
Market Outlook
The global market for medical thermocouple wires is projected to grow from $500 million in 2025 to approximately $850 million by 2033, at a CAGR of 7%. This growth is driven by the rise of minimally invasive procedures and the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases. As more devices incorporate thermocouple sensors, demand will continue to climb.
Alleima’s contribution
Alleima is a leader in medical thermocouple technology, offering vertically integrated manufacturing from alloy melting to finished sensors. Their wires span from AWG24 (0.5104mm) to ultrafine AWG50 (0.0205mm) and are available in various configurations and insulation types. Alleima’s products meet or exceed standards like ASTM E230 and ANSI MC 96.1, ensuring reliability in critical healthcare environments.
With over 200 metals and alloys in their portfolio, Alleima collaborates closely with world-leading OEMs to deliver bespoke solutions tailored to the rigorous demands of medical applications. Their commitment to research and development positions them at the forefront of innovation in temperature sensing technology.
Conclusion
Thermocouple wires may be small, but their impact on medical safety and precision is immense. From cardiac care to oncology, and pain management to critical diagnostics, these sensors enable clinicians to deliver targeted, effective treatments with confidence. As medical technology continues to advance, thermocouples will remain a cornerstone of innovation, quietly powering the future of healthcare.
Meet Alleima at Medical Technology Ireland
Meet our team to explore how Alleima can support your journey – from design and prototyping to commercialization at Medical Technology Ireland, 24-25 September at Galway Racecourse, booth #40.
More information: www.alleima.com/thermocouples
Contact information
Alleima Advanced Materials
1 Commerce Blvd.,
Palm Coast, FL, 32164,
United States
Tel: +1 386 445-2000
Fax: +1 386 447-5113
Email: sales.pc@alleima.com
Alleima Sonceboz
Sur le Brassiège 3
2605 Sonceboz-Sombeval
Switzerland
Tel: +41 32 942 39 20
Email: sales.sb@alleima.com
Alleima Karlsruhe
Wilhelm-Schickard Str. 9c
761 31 Karlsruhe
Germany
Tel: +41 41 761 63 55
Email:sales.ka@alleima.com
Alleima Dettingen
Paul-Lechler-Str.14
72581 Dettingen/Erms
Germany
Tel: +49 7123 91019-0
Email: info.det@alleima.com