COMPANY INSIGHT
Sponsored by Sandvik
EXERA®: Customised wire-configurations for medical device solutions
Marking Sandvik’s entrance into the medical devices sector in which ultra-fine wire is used in the applications, the company introduced EXERA® trademark to wire-based components that are custom made to transmit, sense or stimulate within the human body.
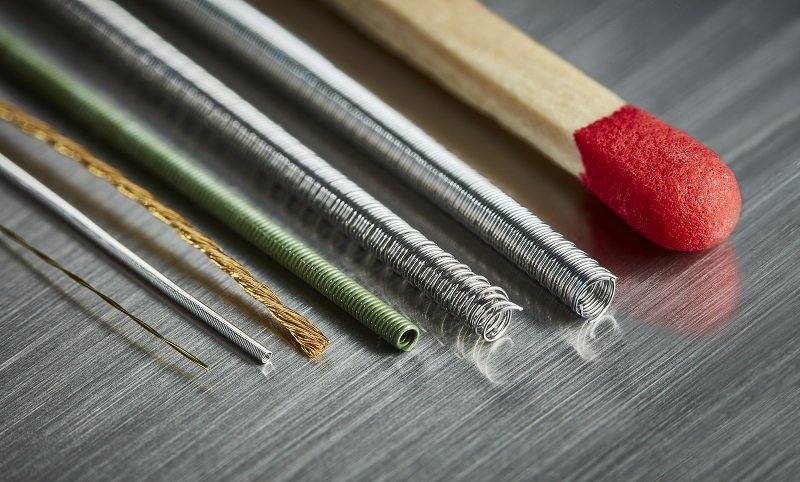

W
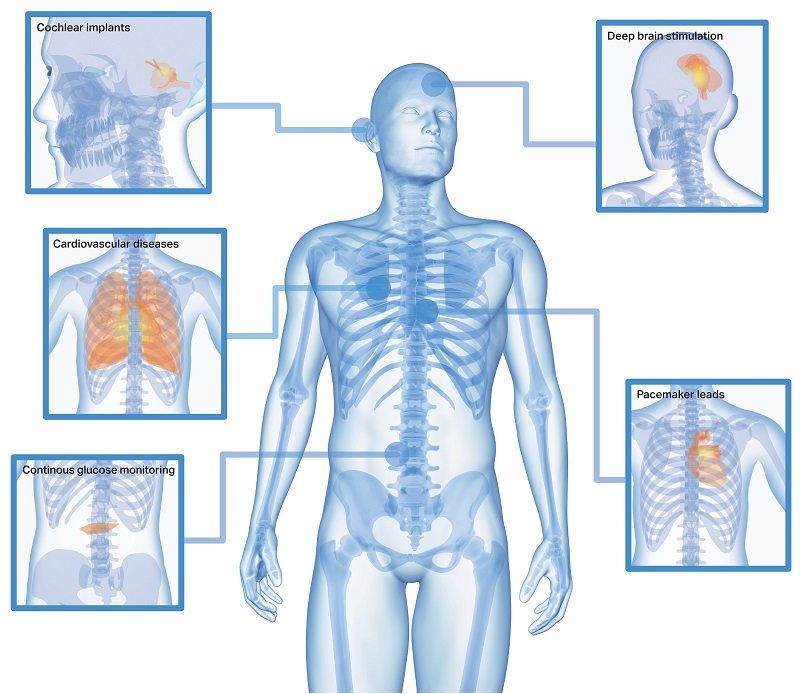
orking with more than 200 alloys, and specialising in choosing the best materials and configurations, EXERA® wire-based components are used for a variety of applications, including vascular therapy, biosensing and neurostimulation. So far, they have been used for devices such as cochlear implants, pacemaker leads, continuous glucose monitors for diabetes care, tremor control for people with Parkinson’s or epilepsy, catheters and guidewires for all kinds of minimally invasive devices.
How do EXERA® products stand out from the competition?
Sandvik Materials Technology’s business area is expert in special steel and alloy manufacturing, drawing on experience that dates back to 1862. Since 2016, their medical business unit who makes EXERA® precison wire components, has been continuing the company’s focus on developing close customer partnerships by offering made-to-order build-to-print solutions, setting them apart from other suppliers.
Extensive experience in material properties not only allows Sandvik to offer customers expert advice on the best components functionality and manufacturing options to reach their end-goal, but also guarantees quality unmatched by the competition.
EXERA® custom wire-components manufacturing
There are unlimited customisations available to customers, and Sandvik is invested in ensuring that the end-product is high-quality, effective and sustainable. Customers can choose from a variety of materials, sizes, surface treatments and product forms. Sandvik also offers small custom melts which speed up the development process. Learn more in the webinar about small custom melts offered by Sandvik
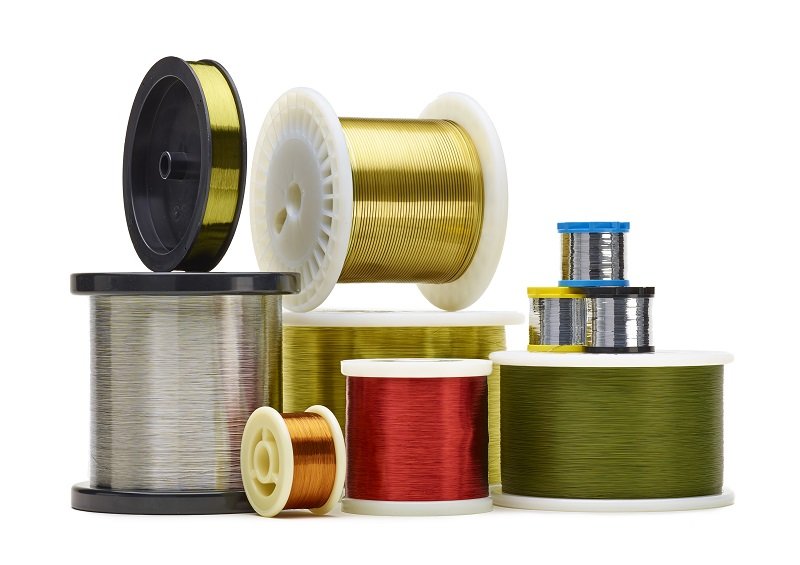
- Regarding the selection of materials, the Sandvik range includes stainless steels (such as EXERA® 12R10 medical wire), carbon steel (such as EXERA® 20AP medical wire), precious metals (including platinum, pure gold and silver), cobalt-chromium-molybdenum alloys (such as EXERA® F562 medical wire), sensor alloys (constantan and copper) and Kanthal® resistance alloys (such as Nikrothal® 80 and Cuprothal® 49).
- Coating: Customisations include base polymer insulation and PTFE coatings to withstand temperatures up to 240°C, as well as solvent or heat activatable bond coatings for free-standing coils or joining wires. The coatings can also be pigmented for identification purposes. Sandvik offers stripping services to remove the polymer coating from the ends of the wire. Learn more about coatings effect on wire-based components in medical devices at the webinar conducted by Sandvik experts

EXERA® medical wire-components, ribbon, multi-filar and stranded cables can be precisely cut to the customer’s requested length. Diameter can range from 0,01mm to 1,0 mm depending on the alloy, shape, temper and required measurement, while length can be between 5 mm to 1800mm, depending on the application. If required, wire straightening can be performed in accordance with ASTM F2819 (unless specified otherwise).
Depending on the size that the customer requires, Sandvik’s medical wire can be delivered in a variety of forms that typically comprise either spools, braider bobbins, straightened lengths or coils. Customised coiling services are offered, ranging from free-standing inductive coils to single/multi-filar helicoil configurations.
Sandvik also offers a range of surface treatments to meet the needs of the customer:
Anodising: For aluminium alloys, reel-to-reel electrolytic passivation enhances the natural oxidation layer, resulting in improved electrical insulation, as well as a more abrasive-resistant surface. It can be applied to round or ribbon wire and the average layer is between 0.005mm and 0.010 mm.
Coating: Customisations include base polymer insulation and PTFE coatings to withstand temperatures up to 240°C, as well as solvent or heat activatable bond coatings for free-standing coils or joining wires. The coatings can also be pigmented for identification purposes. Sandvik offers stripping services to remove the polymer coating from the ends of the wire.
Electroplating and electropolishing: From ultrasonic wire bonding to enhancing electrical properties, Sandvik offers electroplated alloys such as hard and soft gold, nickel and silver for surface finish modification.
When manufacturing medical wire, hygiene is essential, so Sandvik operates in an ISO Class 7 certified cleanroom for various production stages. The environment is fully controlled using HEPA filters, laminar flow cabinets and exhaust hoods to optimise air particle count, air pressure, temperature and any other factor that could affect product quality.
Medical wire applications
EXERA® medical wire-components are customised to feature the properties required for its intended application.
Vascular therapy:
- Catheters and guidewires: Medical wire requires good corrosion and moderate tensile strength, fatigue and relaxation resistance.
- Pacing leads: Medical wire will generally need ultra-high strength, ductility, toughness and very good corrosion resistance.
- EXERA® 12R10 HV medical wire and EXERA® 316LVM medical wire are used for these sensors, catheters and heart mapping/monitoring devices
Cochlear remediation:
- Cochlear implants: Sandvik offers high-quality medical wires produced from platinum-iridium alloys to be encased in the silicone of the implant’s electrode array.
- Middle ear implants: These devices require a tightly coiled metal wire for sound transmission. Sandvik offers coiled wires with a polymer or PTFE coating.
- Bone conducting systems: Medical wire is used in these devices helps transmit energy to the transducer that is directly in contact with the skull.
Sensing solutions:
- Thermocouple: Two or more wires made from different metals are coupled to provide a variable EMF response at different temperatures.
- Glucose sensor: This device requires a fine wire for a sensor thinner than a needle.
- Electrical sensors: Sandvik categorises these devices into multi-electrode arrays and tetrodes.
Stimulation therapy:
- Deep brain stimulations: Sandvik offers high-quality conductive wires with high durability properties. These form an essential part of modern neurostimulation devices.
For more information about EXERA® fine medical wire-components, including a full list of materials or to contact Sandvik about developing a medical field device, visit their website..
Contact information
Sandvik Palm Coast
1 Commerce Blvd.,
Palm Coast, FL, 32164,
United States
Website:exera.sandvik
E-mail:ms.spc@sandvik.com
Telephone: +1 386 445-2000
Fax: +1 386 447-5113
