Insight : Market
Wound care management market overview 2017
Wounds and injuries are common afflictions that affect billions worldwide. Many millions of people suffer from trauma and burns as a result of accidents, natural disasters, and violence. Many more acquire chronic, hard-to-heal wounds due to complications from diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular disease, which are projected to rise dramatically throughout the world in the coming decades.
Ageing populations, which are particularly prone to acquiring wounds, are growing in number, further exacerbating public health problems by driving expenditure and limiting treatment availability. Mechanical wound closure devices and biosurgery brands have been used to stop blood loss and close incisions efficiently. Rising rates of risk factors and the need for cost-efficient treatments are driving the need for better wound care products.
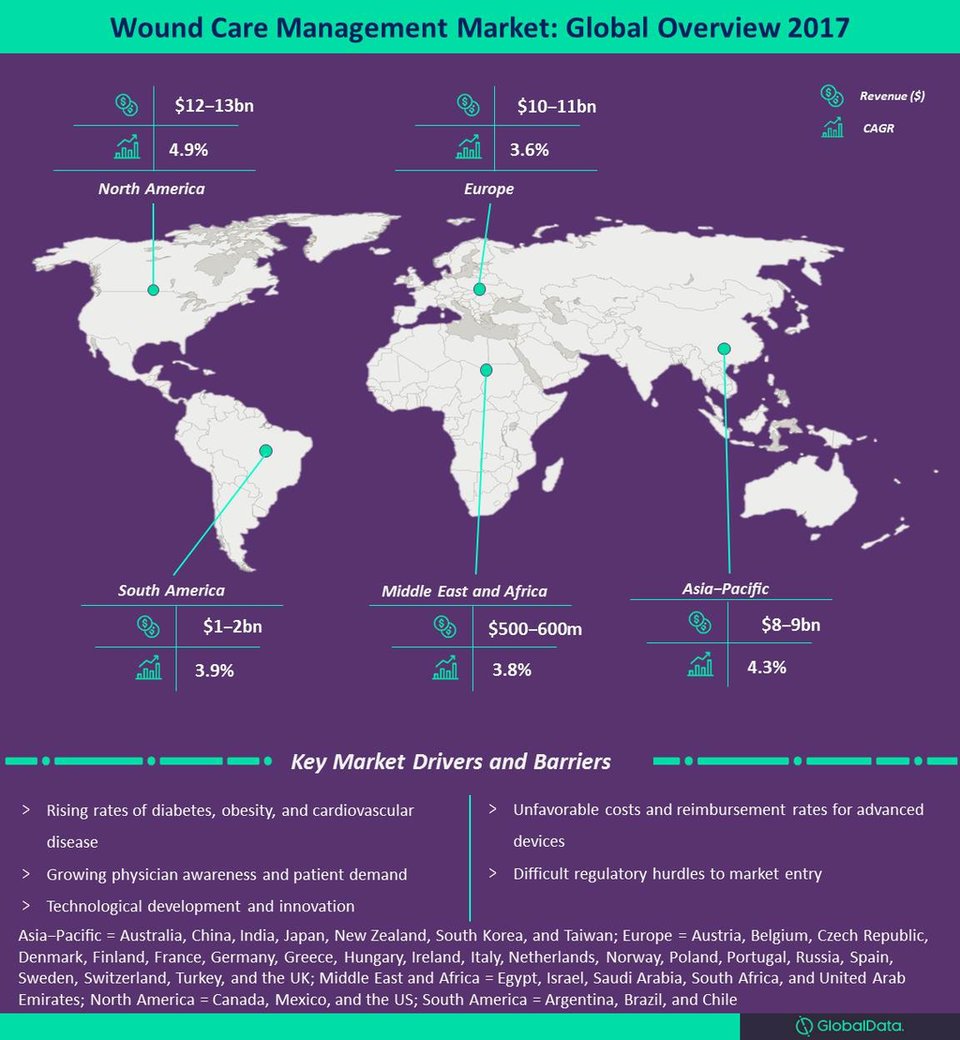
The wound care management market was valued at $33.9bn in 2017, and is expected to expand to $45.5bn by 2024 with a stable compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.3%. Wound therapies have steadily advanced to treat patients more effectively and comprehensively.
Novel formats address all aspects of wound treatment including initial wound closure, debridement, cleansing, moisture absorption and retention, physical protection, and infection prevention and control. Standard treatments such as sutures, dressings, and wound debridement are continuing to work hand-in-hand with advanced therapies to heal wounds completely and without complications.
Advanced wound care products
Advanced products such as biosurgery products, robotic devices for wound closure, tissue engineered skin substitutes, and state-of-the-art wound measurement devices are playing an increasing role in wound healing. Three of the most dynamic markets in the wound care management space are advanced wound closure, negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT), and cellular or tissue-based products.
While the incidence of burns and trauma wounds is decreasing in some markets, the need for fast-acting wound closure products that prevent excessive blood loss and scarring will remain. Combing mechanical methods, including laparoscopic staplers and robotic-assist wound closure devices, with biosurgery products including fibrin-based sealants and combination hemostats, effectively prevents fatal hemorrhaging in the operating room.
Novel inventions and augmentations to existing technology platforms continue to drive the expansion and effectiveness of wound closure products. For example, fibrin sealants have proven to be promising vectors for drug delivery and other bioactive agents such as growth factors to specific target sites in the body.
The NPWT market expanded quickly in 2017, driven primarily by increasing awareness of the technique and its various applications. Disposable, or single-use, NPWT devices are an emerging technology in this space that is expected to see rapid adoption in all countries where they are launched, because of their drastically reduced costs and expanding indications including surgical incisions.
Competition in the market has become intense as more players, such as Medela, Nexa Medical, Stortford Medical, and Genadyne Biotechnologies, have received new device approval. Market leaders such as Acelity and Smith & Nephew remain innovative by upgrading their existing platforms, the V.A.C.ULTA NPWT system and the PICO single use NPWT system, respectively.
Novel therapies, such as products seeded with live cells and wound grafts sourced from amniotic tissue, will gain prominence as clinical evidence becomes more abundant. Cellular products, such as Grafix from Osiris Therapeutics, provide the benefits of fresh placental membrane and reduce inflammation and scarring by supporting wound closure without excessive fibrosis.
More acellular products are available in the market, including NEOX/CLARIX from Amniox Medical, EpiFix from MiMedx Group, and Biovance from Alliqua Biomedical. These acellular products don’t contain active or living cells, but may contain and stimulate growth factors, cytokines, and matrix proteins, providing mechanical substrate for tissue growth. Despite growing demand, these products face market entry hurdles such as high costs and regulatory setbacks.