The impact of artificial intelligence on the medical device sector
AI can automate many routine and administrative tasks for service providers and suppliers, such as updating patient records and streamlining appointments, easing the workload for doctors and nurses, and allowing increased focus on patients. AI can also support the shift from hospital-based to home-based patient care using remote monitoring, wearable devices, and virtual assistants.
There is a huge potential for AI in medical diagnostics. AI-tools can be added to current medical device techniques, such as computerised tomography and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans, for faster analysis of images and diagnoses of diseases, particularly for image-based diagnosis and pathology. AI-based systems can also transform surgical operations.
AI-assisted tools can help surgeons in critical situations where enhanced surgical navigation, object identification, increased imaging details, or spatial understanding can optimise a procedure. AI is also improving the surgical field with remote surgery, where surgeons use robots to perform surgery in a different location to the patient.
The AI-powered Da Vinci robot system, created by Intuitive Surgical, has transformed the field of minimally invasive surgery. These surgeries can reduce human effort, improve patient outcomes, and reduce hospital stays.
The matrix below details the areas in AI where medical device companies should focus their time and resources. We suggest they invest in technologies shaded in green, explore the prospect of investing in technologies shaded in yellow, and ignore areas shaded in red.
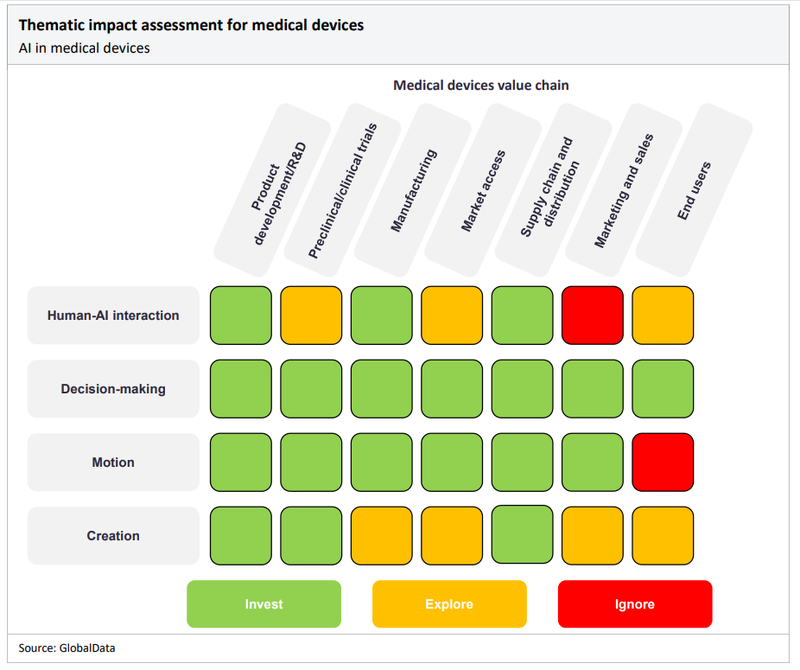
Medical device company investment in AI should not be too dissimilar to that of pharma companies, as the industry is also under pressure to innovate. For manufacturing, AI can assist in quality control to ensure new products are fit for regulatory compliance. AI-enabled equipment can inspect products during the manufacturing process for defects, alert manufacturers of repeated defects, and find the cause of errors.
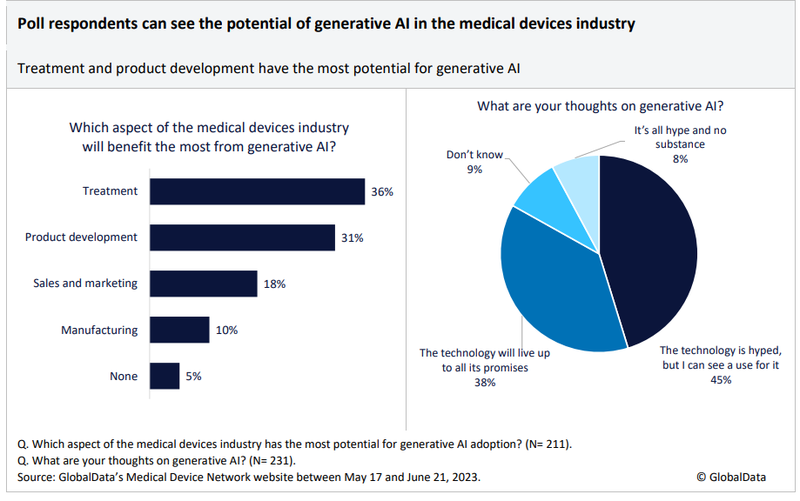
Automating AI to quality-control medical devices can also help the production line increase efficiency over time. Between April 5 and April 25, 2023, visitors to GlobalData’s Medical Device Network were asked which area of the medical devices industry would benefit the most from generative AI. Most respondents selected treatment and product development clinical trials.
Survey respondents were also asked about their overall thoughts on generative AI. Some 83% of respondents saw a use for generative AI in the medical devices industry, with just 8% agreeing that it was all hype and no substance.
Barriers to the uptake of generative AI
According to a GlobalData poll, the risk of incorrect information, risk of misuse, ethical concerns, and cybersecurity risks and concerns are the biggest barriers to integrating generative AI into the healthcare industry. Generative AI is limited by the quality of its training data. Inaccurate responses and misinformation could have devastating consequences for patients.
The use of generative AI in healthcare also raises concerns about protecting patient privacy and sensitive medical data, including using patient data to train generative AI algorithms. Further, generative AI increases cybersecurity risks and the potential for misuse or unauthorised access to healthcare data.
Existing strict regulatory regimes around data privacy in general and healthcare specifically will need to be updated to reflect advancements in AI before generative AI can be trusted in healthcare.
How AI helps resolve the challenge of medical imaging and diagnosis
Radiologists and pathologists routinely evaluate thousands of medical images to identify and diagnose diseases. However, inaccurate and misdiagnoses due to human error or subjective interpretation may impact patient outcomes, especially if the radiologist is overburdened with work.
AI can assist in medical imaging analysis by viewing these medical images, saving radiologists valuable time. AI can distinguish abnormalities from normal findings by detecting minor image alterations, even spotting unseen abnormalities which the human eye cannot identify.
Low-quality images greatly reduce the patient’s standard of care. These often lead to repeat scans, prolonged time to analyse and establish a diagnosis, and increased cost of care. AI can also improve the imaging of low-quality scans, giving healthcare professionals a clearer view of the patient’s pathology and reducing inequalities caused by the disparity of imaging equipment between hospitals and locations.
Researchers at the MIT Jameel Clinic have developed a new AI tool named Sybil to predict the risk of a patient developing future lung cancer within six years. The AI tool analyses low dose computed tomography scans of lungs, currently the most common screening method for lung cancer.
The study, published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, demonstrated that Sybil predicted cancer within one year with an average of 91% accuracy (between three datasets) and 79% accuracy within six years (Mikhael et al., 2023). Although in early stages, this example demonstrates the potential of AI-assisted predictive analysis of diseases.
AI-assisted medical imaging has the potential to revolutionise cancer detection and characterisation. For example, mammograms are routine checks to examine the human breast for early signs of cancer. Scientists created an AI algorithm called Mirai to predict breast cancer risk based on traditional mammograms. The model predicted the risk of developing breast cancer in the next five years more accurately across various tests than current tools (Yala et al., 2021). As a result, high-risk identified patients can then routinely screen for breast cancer more frequently for earlier detection of the disease.
AI has also shown the potential to improve cancer detection in patients with symptoms. AI can monitor patients more thoroughly and track even the smallest changes in conditions and tumours, helping predict the likelihood of cancer spreading. This information can also help patients receive a more personalised treatment plan.
How AI helps resolve the challenge of supply chain disruption
Efficient supply chains are integral to healthcare systems, ensuring that medical supplies and services are delivered to patients. The complex nature of healthcare supply chains means manufacturing, distribution, and delivery efficiency is essential. These supply chains involve multiple participants and can impact patient safety and health-related outcomes in often time-sensitive medical products and devices.
The Covid-19 pandemic exposed vulnerabilities in the healthcare supply chain and led to a global shortage of medical products. Healthcare supply chains are now under increasing pressure due to rising demands for medical products, the cost of supplies, increasing competition, and the need to prepare for future pandemics. Therefore, embracing technological advances is crucial for supply chain efficiency and productivity.
Automation with AI can be used across various parts of the supply chain to reduce costs, improve efficiency, and alleviate staff pressures, especially where there are staff shortages. AI can automate the process of tracking, forecasting, and managing inventory. For purchasing medical supplies and products, automated purchasing systems can use AI to analyse previous trends in purchasing data to identify opportunities for reducing costs and negotiating better deals.
AI-powered systems can increase accuracy by identifying order errors and detecting fraudulent activity. In hospitals and clinics, AI monitors the expiration dates of products and provides real-time data on inventory use. When stocks reach a certain level, automated replenishment systems use AI to reorder supplies.
For delivery, some healthcare facilities have adopted AI-powered robots and drones, increasing the speed of delivery of supplies and medication to patients. AI can also increase the efficiency and cost of delivery systems by finding optimal routes for transportation and tracking shipments.
Manufacturing robots with AI capabilities can help companies establish agile, cost-effective, and robust processes that are coordinated across the supply chain. AI-powered warehouse tools speed up communication and reduce errors by predicting which items need downtime or repairs.
In addition, AI-powered digital twins can monitor and identify optimal production processes or create virtual training platforms for employees. AI can also improve medical device manufacturing efficiency and reduce risk. Through machine learning (ML), computers are taking in troves of data and learning errors while enhancing engineers' jobs in the manufacturing process.
Predictive analysis is also a crucial AI application for healthcare supply chains. AI can analyse large volumes of data, using past data to predict future events. This can help to determine the effectiveness and cost of current products and predict which products will be more valuable for formularies and healthcare plans.
More accurate supply forecasts help to reduce inventory run outs and the expiration of current supplies, especially where there is an oversupply. This can also help with supply continuity, helping hospitals and other care centers manage backlogs and find clinical alternatives if there is a shortage. Predictive analysis helps to mitigate risks and the impact of supply chain disruptions on the healthcare industry.
GlobalData, the leading provider of industry intelligence, provided the underlying data, research, and analysis used to produce this article.
GlobalData’s Thematic Intelligence uses proprietary data, research, and analysis to provide a forward-looking perspective on the key themes that will shape the future of the world’s largest industries and the organisations within them.